Isoptin ER (Verapamil ER) Tablet ER
Branded
Generic
Verapamil ER (Generic Equivalent to Isoptin ER)

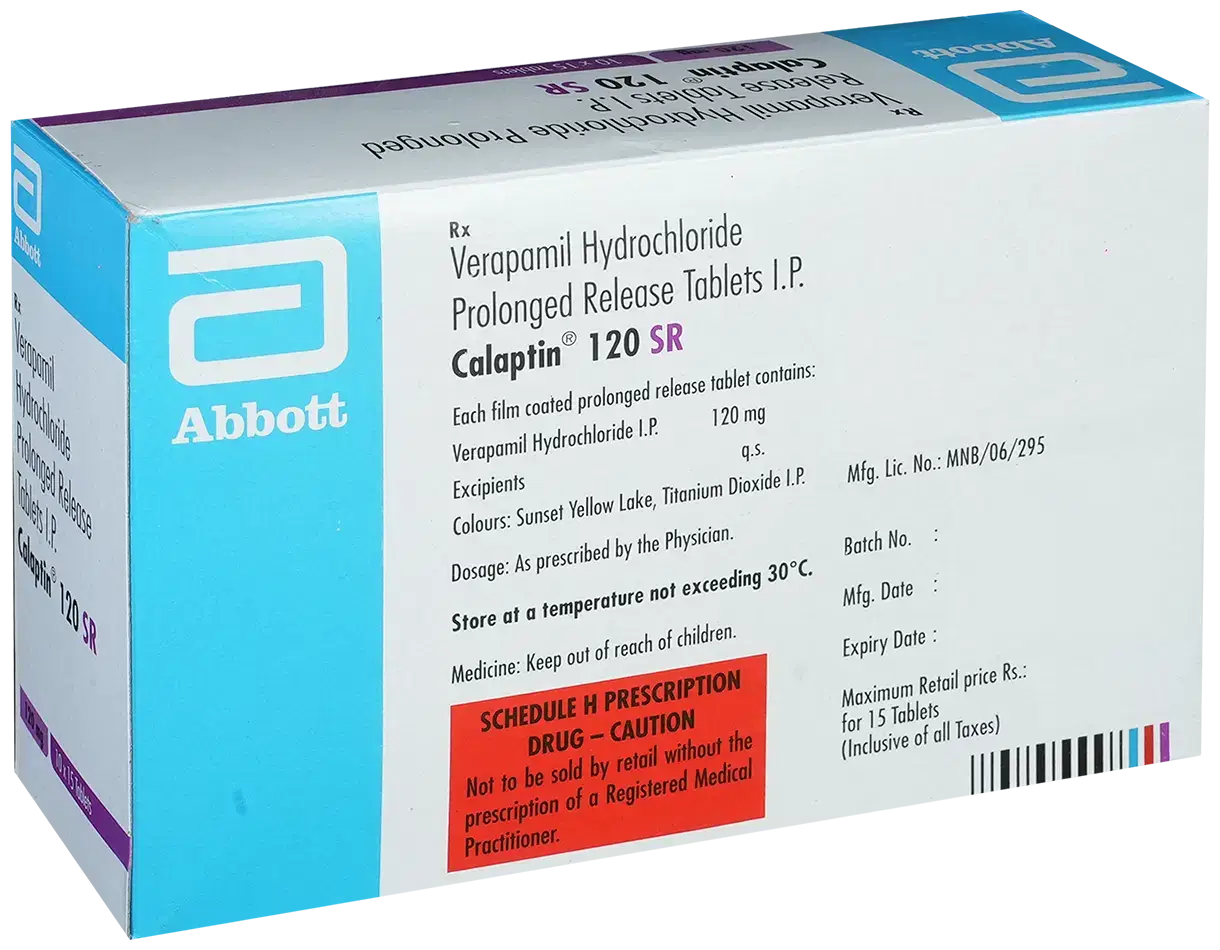

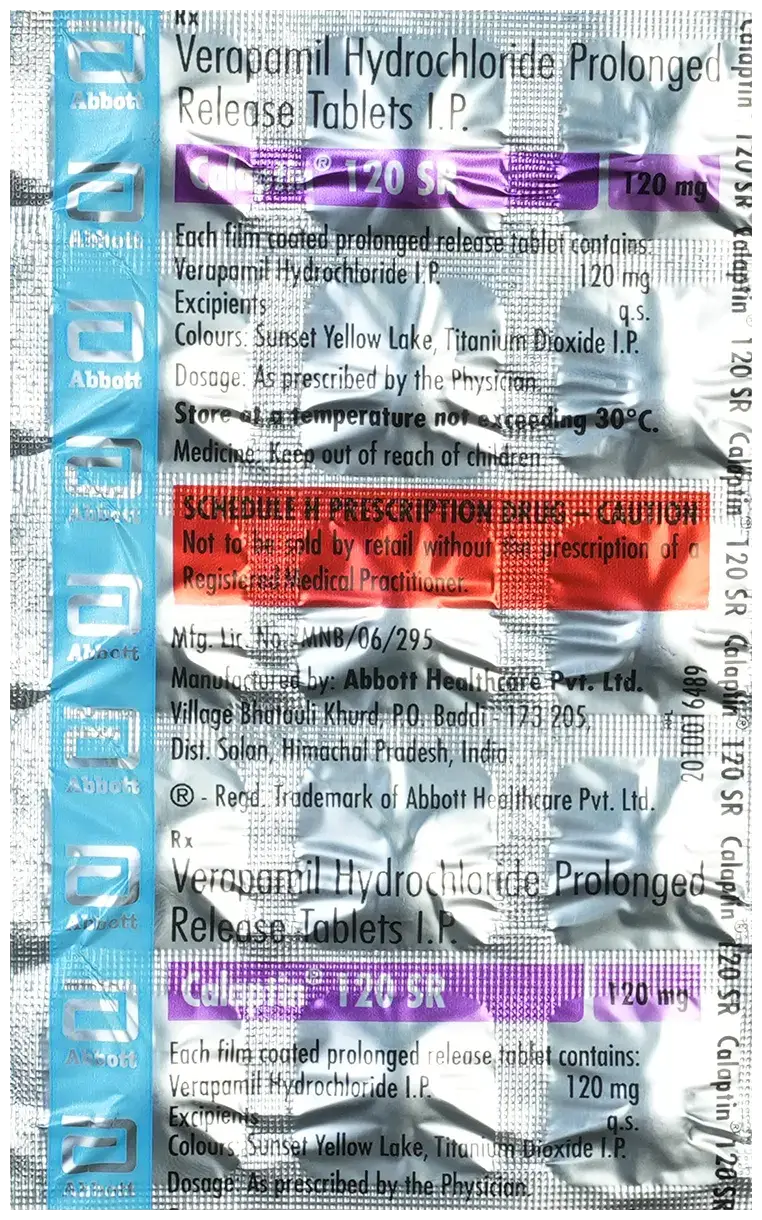
Verapamil ER (Generic Equivalent to Isoptin ER)




Isoptin ER Tablet ER is used to treat angina (heart-related chest pain), high blood pressure, and some types of irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia). It works by relaxing blood vessels to lower blood pressure. This helps to reduce the workload of the heart.
Isoptin ER Tablet ER may be taken with or without food, but it is better to take it regularly at a fixed time each day as advised by your doctor. Keep using this medicine even if you feel well. If you stop taking it suddenly, your condition may worsen. This medicine is only part of a treatment program that should include a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight reduction as advised by your doctor.
The most common side effects of this medicine include constipation, dizziness, nausea, hypotension, and headache. These are usually mild and disappear after a short time. Consult your doctor if they bother you or do not go away. Drinking alcohol should be avoided while taking this medicine as it may worsen the side effects.
Before taking this medicine, let your doctor know if you have any liver or kidney problems. Also, inform your doctor if you have very low blood pressure (hypotension), heart failure, or if you recently had a heart attack and have fluid in your lungs. Your doctor may want to monitor your blood pressure while using it and you may need frequent blood tests. Pregnant or breast-feeding women should consult their doctor before taking it.
Uses Of Isoptin ER Tablet ER
- Treatment of Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Treatment of Angina (heart-related chest pain)
- Treatment of Arrhythmia
Benefits Of Isoptin ER Tablet ER
In Treatment Of Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Isoptin ER Tablet ER works by relaxing blood vessels so that blood can flow more easily around your body. This lowers your blood pressure and reduces your risk of having a stroke, heart attack, or kidney problems in the future. It must be taken regularly as prescribed to be effective. You do not usually feel any direct benefit from taking this medicine, but it works in the long term to keep you well. Do not stop taking this medicine without your doctor’s advice, even if you feel well.
In Treatment Of Angina (Heart-Related Chest Pain)
Isoptin ER Tablet ER helps treat heart-related chest pain (angina attack) as well as prevent it from happening in the future. However, it should not be used for acute attacks of angina. It works by relaxing and widening blood vessels in the heart. This makes it easier for blood to flow to the heart, so it gets more oxygen. This medicine thus helps to increase your ability to exercise and go about your daily life more easily and confidently. It should be taken regularly to be effective. Do not stop taking it without your doctor’s advice, even if you feel well.
In Treatment Of Arrhythmia
Isoptin ER Tablet ER may also be used to treat abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia). It may help stop an abnormal rhythm while it is happening or prevent its occurrence in the first place.
Side Effects Of Isoptin ER Tablet ER
Most side effects do not require any medical attention and disappear as your body adjusts to the medicine. Consult your doctor if they persist or if you’re worried about them
Common Side Effects Of Calaptin
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Headache
How To Use Isoptin ER Tablet ER
Use it as advised by your doctor or check the label for directions before use. Isoptin ER SR Tablet ER is to be taken with food.
How Isoptin ER Tablet ER Works
Isoptin ER Tablet ER is a calcium channel blocker. It blocks the action of calcium on the heart and blood vessels, thereby widening the blood vessels and allowing more blood and oxygen to reach the heart. This reduces blood pressure and decreases the chances of angina (chest pain).
Disclaimer :The information provided on the website is intended to facilitate awareness about healthcare products and medical conditions generally but it is not a substitute for professional medical attention or advice. You should always speak with a qualified healthcare practitioner before taking any prescription or non-prescription drug. |
| Product Type--Salt | Generic–Verapamil ER (Generic Equivalent to Isoptin ER) |
|---|---|
| tag--Manufacturer | Best Selling–Abbott, Best Selling–Abbott, Best Selling–Zydus Healthcare |
| Power--Pack Size | 120mg–30 Tablets ER, 120mg–60 Tablets ER, 120mg–90 Tablets ER, 120mg–180 Tablets ER, 240mg–30 Tablets ER, 240mg–60 Tablets ER, 240mg–90 Tablets ER, 240mg–180 Tablets ER, 240mg–30 Tablets ER, 240mg–60 Tablets ER, 240mg–90 Tablets ER, 240mg–180 Tablets ER |
Related products
- Login
- Sign Up
